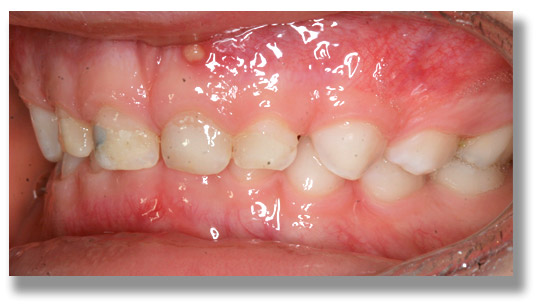
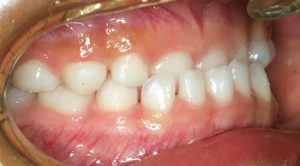
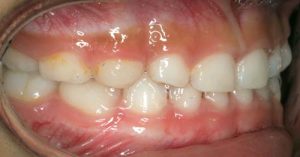
We learn from recent evidence that there is a direct correlation between gum disease and cardiovascular (heart) disease. Bacteria from diseased gum pockets including their toxins have been found in the lining of the heart and of major arteries. Infected pockets often involve many, sometimes dozens, of pathogenic bacteria, fungi, and even parasites (protozoa). Research has shown that patients with gum disease are more likely to suffer from heart disease, to suffer heart attacks or strokes, and to contract diabetes.
Gum disease is a CONTAGIOUS disease affecting the WHOLE BODY. In fact, every time a person with gum disease brushes, flosses, or has teeth cleanings done, millions of bacteria and parasites enter the blood stream and can end up in diseased joints, arteriosclerotic plaque, the kidneys and heart. Bacteria involved in gum disease also produce organic compounds, which react with the mercury found in amalgam fillings, thus creating the most toxic form of mercury.
In our office, we take periodontal disease very seriously, and consider it a systemic disease. Treatment is based on biological principles, and involves up to 3 phases, with regular appointments. The treatment outcome depends a lot on patient compliance and motivation. We urge you to have a full medical and cardiological exam by your physician, including blood, urine, and heavy metal analyses.
The following supplements are recommended for patients with periodontal disease:
Vitamin C: 2000 mg twice daily.
Selenium: 200mcg daily. (Do not take at the same time as Zinc)
Omega fatty acids, Vitamin E and garlic oil
Glutathione: 150mg daily
Coenzyme Q10: 50 mg daily
Anti-inflammatory enzymes (e.g. Infla-zyme forte, Wobenzyme, etc.) 4 tablets between meals twice daily.
Zinc gluconate or picolinate: 30 mg daily half hour before bedtime.
Also
- Rinse twice daily with an herbal mouthwash, and nights with 3% hydrogen peroxide after brushing.
- Brush and floss twice daily in front of a mirror, following your new instructions.
- Under-the-gum irrigator: Dilute ½ capful in 3 oz of water, draw into the syringe provided, screw on the plastic irrigating tip, and irrigate the deep pockets as demonstrated by the hygienist.
- Cut back on frequent snacks with sweetened or refined foods. Increase fiber intake.
- Do not share utensils with other family members, and wash thoroughly with hot water.
- Other family members must be treated simultaneously, to eradicate the microbes from the household, and to avoid re-contamination.